Lightning is one of nature’s most powerful and destructive forces. In India, where monsoon seasons bring intense thunderstorms. Every year, Lightning strikes damage electrical equipment and buildings to the tune of billions of rupees annually, Protecting your property from lightning is crucial , in which Lightning protection system (LPS) is your first line of defense, and at the heart of this system is the lightning arrester, it’s not just an accessory but a critical safety necessity for any structure. But with different lightning arrester types available, choosing the right one for your home or commercial building can be confusing. This guide will help you understand all you options.
To assist you in making an informed choice. Therefore, this comprehensive guide from ADASEarthlink will delve into the various lightning arrester types and break down their working principle, clear up the common confusion between lightning arresters and surge arresters, and guide you through their installation and testing of lightning arrester. Whether you are a homeowner, a building manager, or simply keen on electrical safety, this guide equips you with the knowledge to protect your property and loved ones., and give you a clear overview of lightning arrester installation.
What is a Lightning Arrester? Understanding its Critical Function
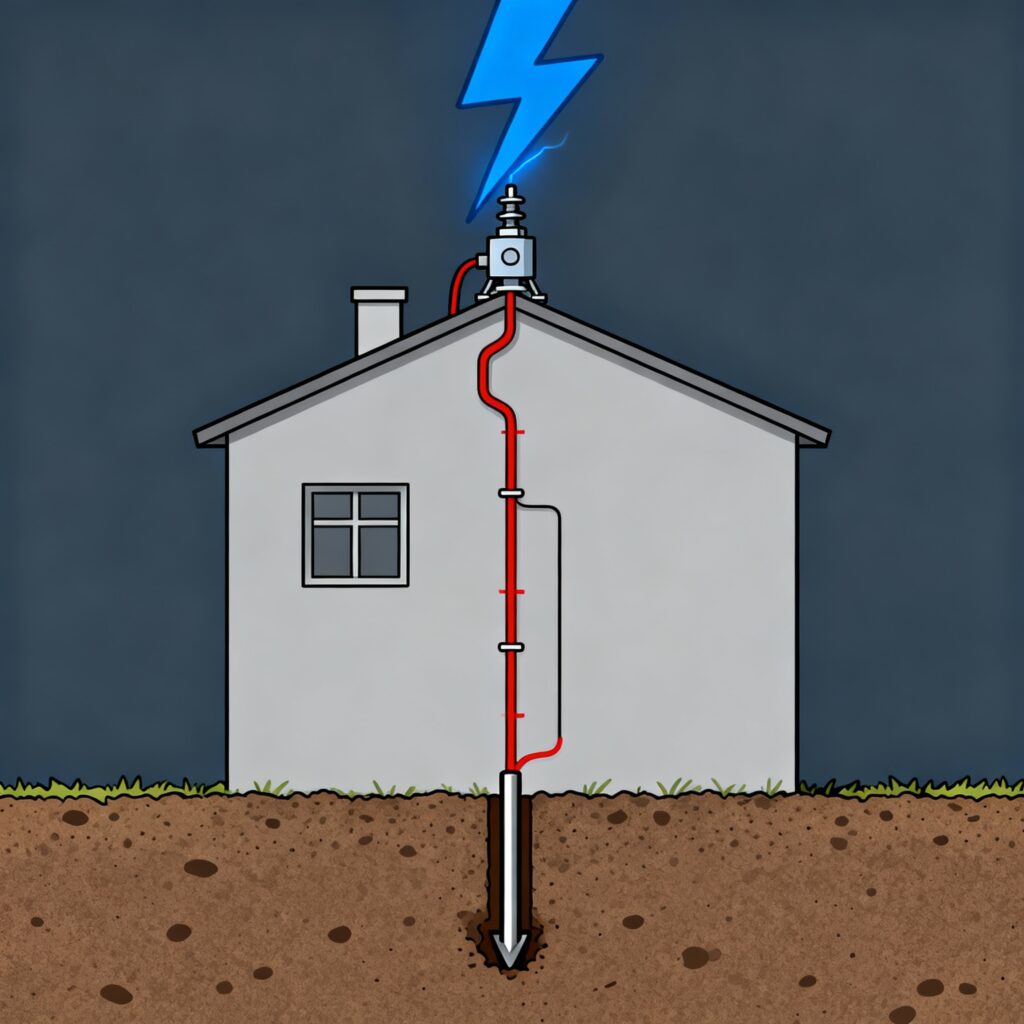
It is a crucial device installed on electrical systems and structures to protect them from the devastating effects of lightning strikes and voltage surges. Specifically, It’s primary function of lightning arrester is not to stop lightning but to provide a safe, controlled path for the massive electrical surge to flow directly into the grounding system, bypassing your valuable appliances and wiring.
Think of it as a pressure relief valve. Under normal conditions, it does nothing. But when a dangerous over-voltage occurs, it activates instantly to divert the harm away.
This process prevents the surge from flowing through the electrical wiring of a home or building, thereby preventing fires, explosions, and destruction of expensive electronic equipment
Lightning Arrester Working Principle: The Science of Protection
The lightning arrester working principle is based on providing a low-resistance path to the ground only during a surge. Typically, inside the arrester, there is a series of components (often made of metal oxides) that have a very high resistance under normal voltage.
However, when a surge voltage exceeding the normal threshold occurs (e.g., from a lightning strike), this resistance breaks down instantly. As a result, this creates a short circuit to the ground, channeling the surge current away from the equipment. Finally, once the surge passes, the arrester returns to its high-resistance state, cutting off the follow-on current and allowing the system to operate normally again.
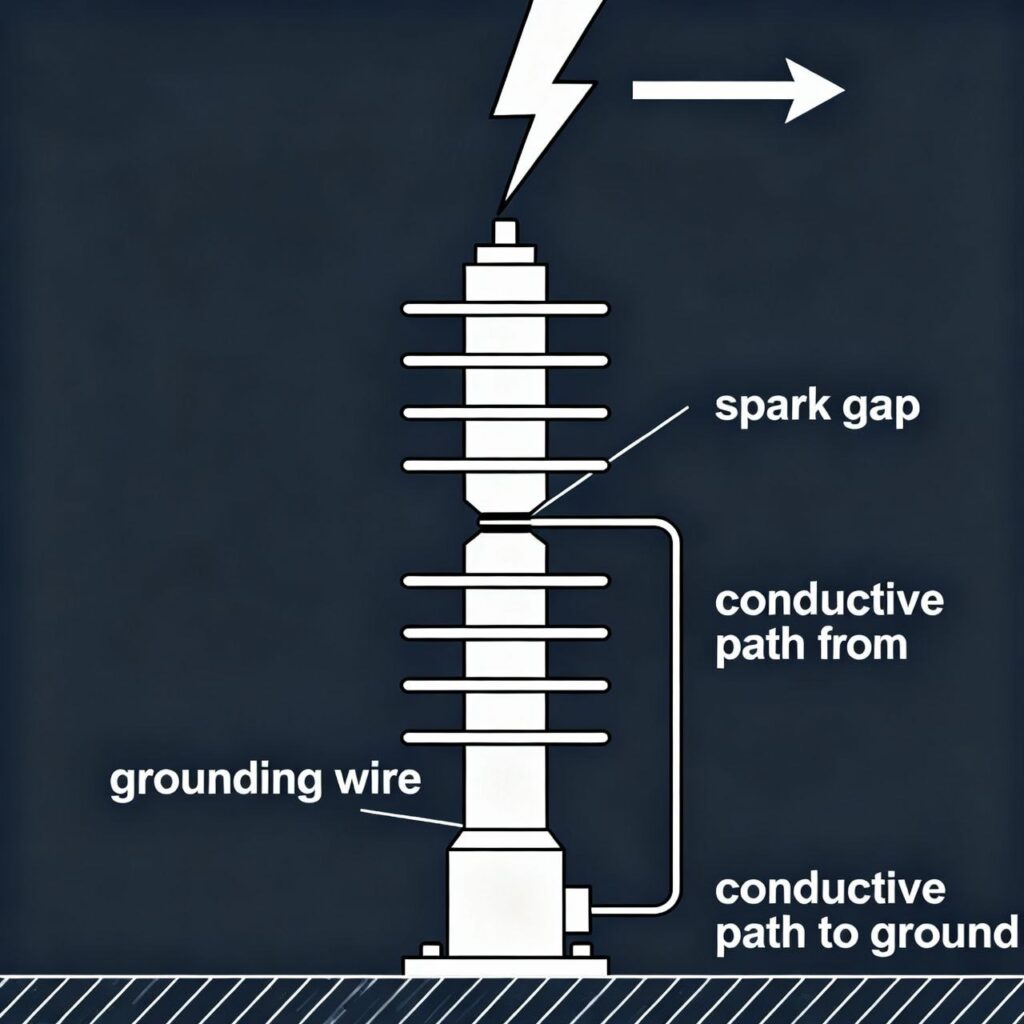
In briefly, Under normal operating conditions, the arrester presents a very high resistance and is virtually invisible to the system. However, when a lightning-induced or other voltage surge travels along the conductor, the arrester detects this dangerous spike.
It momentarily “breaks down,” creating a low-resistance path that allows the high-voltage surge to be discharged directly to the ground. Once the surge is dissipated and the system voltage returns to its normal level, the arrester automatically restores its high-impedance state, stopping the flow of current to the ground and allowing the system to resume normal operation. This entire process happens in microseconds.
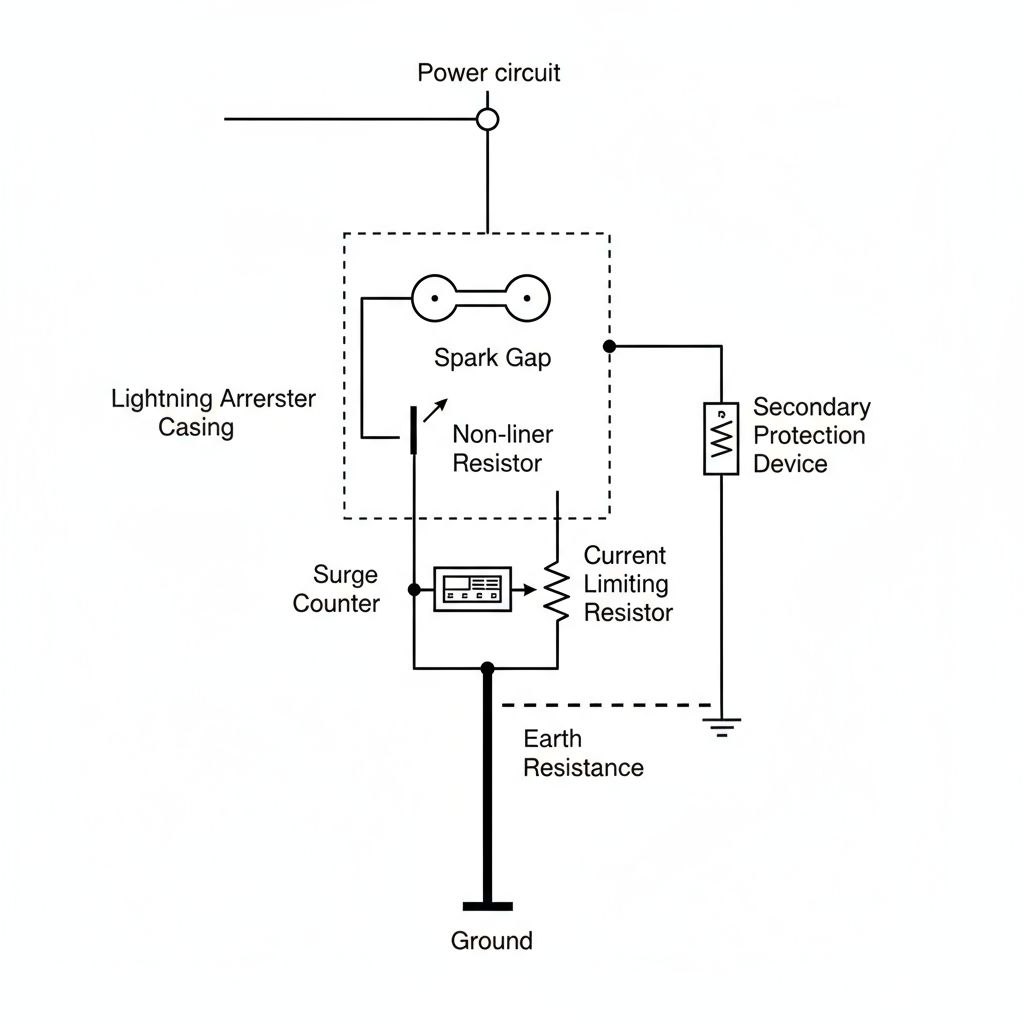
The Anatomy of an Ideal Lightning Arrester
An ideal lightning arrester possesses several key characteristics to be effective and reliable:
- Precise Spark-Over Voltage: It must activate at a voltage high enough to ignore normal system fluctuations but low enough to operate before the protected equipment is damaged.
- Rapid Response: It must break down and start conducting almost instantaneously when a surge occurs.
- High Surge Current Handling: It must be capable of carrying the massive current of a lightning strike without being destroyed.
- Automatic Recovery: After the surge passes, it must immediately restore to its non-conducting state to prevent power flow to the ground.
- Durability: It should be capable of performing its function multiple times over its lifespan.
Types of Lightning Arresters
Several types of lightning arresters have been developed over time, each with its own construction and advantages. The selection of a lightning arrester depends on various factors such as voltage, current, and reliability.
Lightning arrester types include:
- Road Gap Arrester
- Multiple-Gap Arrester
- Horn Gap Arrester
- Sphere Gap Arrester
- Metal Oxide Lightning Arresters
- Valve Type Lightning Arresters
- Oxide Film Arrester
- Impulse Protective Gap
- Electrolytic Arrester
- Expulsion Type Lightning Arrester
- Thyrite Lightning Arrester
- Auto valve Arrester
- ESE (Early Streamer Emission) Lightning Arrester
Understanding the different types of lightning arresters is essential for choosing the right one for specific applications.
Here we will discuss a few of the lightning arresters in detail below
1. Rod Gap Arrester
A simple and outdated category consisting of a gap between two rods. Specially, it consists of a gap between two rods. When a surge occurs, it jumps the gap to earth. It’s imprecise and can be slow to operate
2. Expulsion Type Arrester
Uses a fiber tube that produces a gas to extinguish the arc after the surge passes. Often used for older, outdoor power line protection.
3. Valve Type Arrester: The Modern Standard
Among all options, this arrester represents the most common choice for modern high-voltage systems. Notably, It uses a non-linear resistor (like a zinc oxide block) that offers very high resistance normally and very low resistance during a surge. As a result, they are highly effective and reliable. Additionaly, they operate very quickly and require no maintenance, making them sutable for both indoor and outdoor use. Therefore, This makes valve type arresters the industry standard for most application
4. ESE (Early Streamer Emission) Lightning Arrester: For Extended Protection
It’s an advanced, active arrester for building protection. Despite the advantages of valve type, it claims to have a longer “capture range” than a standard air terminal, creating a larger zone of protection. Therefore, This makes it a popular ESE lightning arresters for protecting large structures like factories, hospitals, and residential complexes.
· For a full breakdown of how an LPS works, read our guide on What Is A Lightning Protection System?
Advantages and Disadvantages of Lightning Arrester
Advantages:
- Reduces Property Damage: Significantly lowers the risk of fire and structural damage from lightning currents.
- Protects Electrical Equipment: Prevents costly damage to appliances, wiring, and other electronic devices.
- Enhances Safety: Mitigates the risk of fatal electrocution to occupants by preventing surges from entering the electrical system.
- Prevents Electromagnetic Interference: Shields sensitive communication and electronic equipment from the electromagnetic pulses generated by lightning.
Disadvantages:
- Requires Space: The system, including grounding, requires adequate physical space for proper installation.
- Initial Cost: The device and its professional installation involve an upfront investment.
- Maintenance: Requires periodic testing and inspection to ensure it remains functional.
Surge Arrester vs. lightning Arrester: What’s the difference?
This is a common point of confusion. While both protect against over-voltage, they are designed for different threats:
KEY POINTS:
- Lightning Arrester: Designed to handle the massive, high-voltage current of a direct or nearby lightning strike. It is installed at the origin of the electrical service (e.g., main panel) or on the roof as part of an external LPS.
- Surge Arrester (or Surge Protector): Designed to handle smaller, more frequent voltage surges from within the power grid (e.g., from motors or transformers switching). They are installed at sub-panels or point-of-use for delicate electronics.
Location and Installation of a Lightning Arrester for Home and Building
location of a lightning arrester:
The location of a lightning arrester is critical to its effectiveness. It must be installed as close as possible to the entry point of the conductors it is protecting.
- In AC Systems: It is connected between the phase (live wire) and the ground.
- In DC Systems: It is connected between the pole and the ground.
For a home, this means at the main electrical service panel. For a building, arresters may be needed at the main service head, near generators, and on sub-distribution boards. Lightning arrester installation is a complex and safety-critical task. It involves working with high voltages and creating a proper grounding system, so it must always be performed by a licensed and experienced electrician.
The process varies for external and internal arresters. To ensure proper installation, follow these steps,

Lightning Arrester Installation Steps:
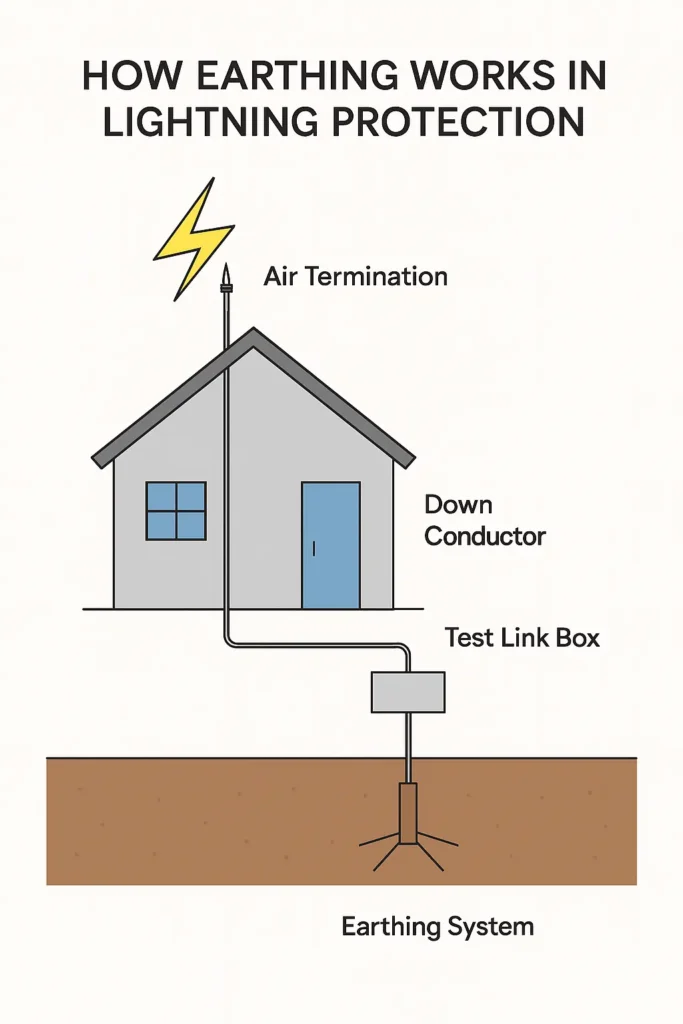
For an External LPS (on the building structure):
- Firstly, arresters (air terminals) mount on the highest points of the roof.
- Then, they are connected via down conductors that run along the walls.
- Most importantly, all down conductors must terminate into a low-resistance earthing system comprising earth rods and a grounding grid.
The entire system relies on this. Learn more in our article on What Is Earthing in Electrical Systems?
The connection point is often a test link box. Learn its role here.
For an Internal Arrester (at the electrical panel):
- Firstly, Licensed electrician must perform installation.
- Then, It is wired in parallel between the phase conductor and the ground terminal.
- Most important, the earthing system must be impeccable, often using high-performance copper bonded earth rods.
- We recommend these rods for their reliability. See our types of copper bonded earth rods article.
Lightning Arrester for Home vs. Lightning Arrester for Building
How to Test a Lightning Arrester
Regular testing of a lightning arresters is vital to ensure it will operate correctly when needed. Common testing methods include:
- Visual Inspection: Checking for physical damage, cracks, or corrosion.
- Insulation Resistance Test: Measures the resistance of the arrester’s insulation to ensure it is not compromised.
- Power Factor Test / Dielectric Test: Assesses the condition of the internal insulation and components to detect any deterioration.
Specialized equipment is needed for these tests, which are typically carried out by certified electrical maintenance professionals.
CONCLUSION: SECURE YOUR PROPERTY WITH THE RIGHT PROTECTION
In an era where our homes and buildings are filled with sensitive and expensive electronics, a lightning arrester is no longer optional but essential. Understanding its working principle, the different types available, and the distinction from a surge arrester empowers you to make the right safety decisions for your property.
By investing in a properly designed, ensuring its professional installation under safety guidelines for electrical installations , and maintained system, you are not just protecting bricks and mortar; you are safeguarding your financial investment, your data, and, most importantly, the lives inside. Thus, we strongly recommend consulting with experts to ensure optimal protection for your property. Get touch in now!
Lightning Arrester: Working Principle, Types, and Installation
Lightning is one of nature’s most powerful and destructive forces. In India, where monsoon seasons…
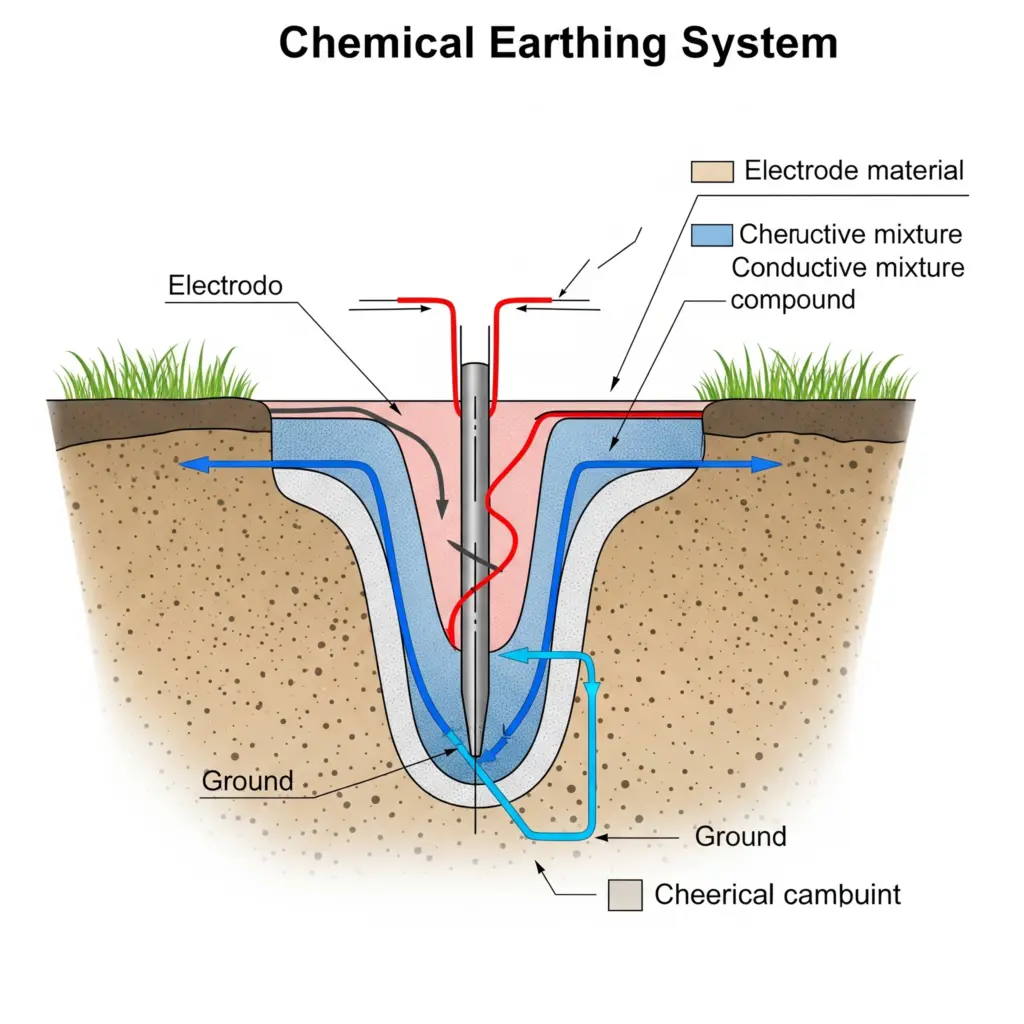
What is Chemical Earthing: Uses, Types & Specifications
In our everyday lives, we often overlook the intricate systems that work silently to keep…
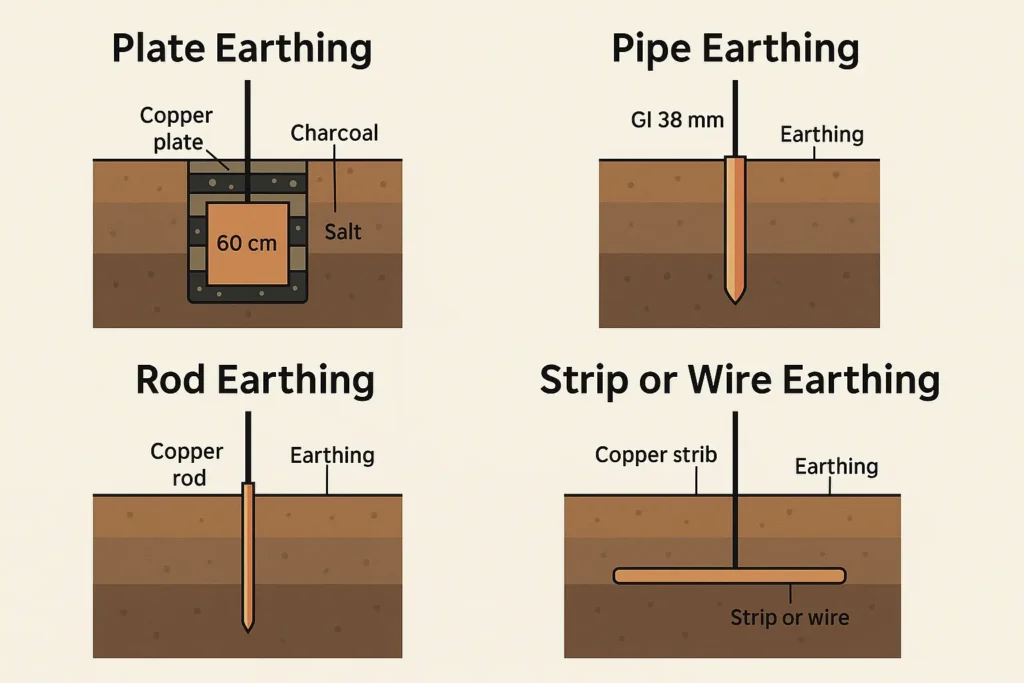
How Many Types of Earthing Are There?
One of science’s wonderful gifts is electricity as it lights up our TV, Fans, ACs,…
Importance of Earthing in Lightning Protection Systems
Lightning is one of nature’s most powerful and unpredictable forces. A single lightning strike can…
What Is a Test Link Box in Lightning Protection Systems?
Lightning protection systems (LPS) are critical for safeguarding buildings, equipment, and lives against the destructive…